- Polynomial.js
- Fraction.js
- Matrix.js
- Vector.js
- ComplexNumber.js
- BigIntType.js
- BigIntFractionComplex.js
- functions.js
WIP
- formula for degree 3/4
- chainable methods
- make polynomial directly/from string/roots
- print as string
- finding roots
- Newton's method for degree 3 and higher
- formula for degree 2 and lower
- create derivative/antiderivative
- calculate f(x)
- calculate integral with
- antiderivative formula
- set delta x
- make fraction directly/from decimal/-string
- GCD & decimal to fraction algorithm as public static methods
- fraction to
- improper-form
- mixed-form
- decimal
- string
- addition/multiplication/subtraction/divition with
- a single integer
- another fraction
- raise fraction to nth power
- chainable methods
WIP
- row to row addition
- row to row subtraction
- row multiplied by constant
- make matrix directly/from string
- create identity matrix
- print as a formatted string
- single number
- muliplication
- divition
- matrix
- addition
- subtraction
- multiplication
- divition
- matrix inversion (Gauß Bareiss)
- chainable methods
- row
- move
- delete
- col
- delete
- check matrix stats
WIP
- make vector from string
- printing to string
- 1D, 2D or 3D vector
- calculate length
- calculate angle
- to other vector
- to X, Y, Z - axis
- to XY, YZ, XZ - plane
- to X, Y, Z - axis on XY, YZ, XZ - plane (2D>3D)
- static methods DEG to RAD and RAD to DEG conversion
- test if finite
- test if equal to another vector
- convert vector to unit-vector (length 1 same direction)
- vector
- addition
- subtraction
- inversion
- scale by constant (multiply number)
- make a complex number with
- real and imaginary part
- with length and angle
- radian
- degree
- square rooting a negative number
- raising e to i-times-n-th power (
e^(i*n)) - raising n to power of i (
n^i)
- getter for
- real part
- imaginary part
- angle (radian or degree)
- length / absolute value
- arc length (from
0r/0°to where the complex number is)
- check for equality
- chainable methods
- logging current value without braking method chain
- create a copy of the the current complex number and continue with it
- complex number
- addition
- subtraction
- multiplication
- division
- raising current complex number to nth power
- static values for
2ππ/2π/4e^ii^i
WIP
- custom PRNG for
randomInt()BigIntTypeas type for bitshift methods- new special case for internal division algorithm
arbitrary precision integer using JS's Uint8Array (unsigned 8-bit integer array) human "readable" code with lots of documentation (js-doc & some comments) and descriptive error throws
- adjustable limit
MAX_SIZE:Number(Range 1 to 67108864 / 64MiB) (software max is [8PiB-1] - wich could be extended to [16PiB-2] usingUint16Array- or even [32PiB-4] usingUint32ArrayandBigInt) - internal values:
sign:Boolean/digits:Uint8Array(base 256 digits) /length:Number(length of digit-array) - during JS type coercion, it converts to
BigIntby default or in the context of numbers and to (base 16)Stringwhen used in the context of strings - conversions to
toBigInt()/ToNumber()/ToString(base) - can be created from, and converted to, different bases
- encode
toURL()/fromURL() - comparisons:
isOdd()/isEven()A === 0/A === 1/A === 2A < B/A > B/A == B/A === B/A >= B/A <= BisSafeInteger()/isFinite()(for checking if its save to convert toNumber)isPowerOfTwo()/isPowerOfBase()(256)
- chainable methods:
- number constants:
0/1/2also negative equivalents andInfinity(1 ** 1024) /MAX_VALUE/HelloThere - logging to console via
logConsole(base)format:[timestamp] (byte count) sign digits (base indicator)(text is green on black and in large monospace font if the console supports it) - copy/setEqual:
copy()/reverseCopy(toOtherNumber)/setEqualTo(otherNumber)/swapWith(otherNumber) - sign:
abs()/neg()(-A) /signNum()(+1 / +0 / -1) - operations:
- bitwise operations:
A >>>= x/A <<= x/A &= B/A |= B/A ^= B/A ~= A
GCD(A, B)mapRange(a, b, a2, b2)with rounding and limit (cap at a2 / b2)
- number constants:
randomInt(min, max)(usingMath.random())- ↑ (
AandBare typeBigIntTypeandxis typeNumber) ↑
ALL YOUR BASE ARE BELONG TO US
- all bases from 2 to 4'294'967'296 (inclusive) are supported for in- and output
- via
String,Number,BigInt,Uint8Array, or array ofNumbers - base 1 is only supported for input
- via
- supported prefixes
0bfor base 2 (binary)0ofor base 8 (octal)0xfor base 16 (hexadecimal)
- used characters (as digits in a string)
- up to base 36 (including),
0-9andA-Zare used as needed - above 36 only via CSV (comma-separated-values or numbers in this case),
where each number corresponds to the numerical value of the digit at that place
(in base 10 / with
0-9) "braille"is in base 256 but uses braille patterns (U+2800toU+28FFinclusive) as digit-charset
- up to base 36 (including),
click to show table
| base | names | base | names |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | b / bin / bits / binary / 1bit |
72 | duoseptuagesimal |
| 3 | ternary / trinary |
80 | octogesimal |
| 4 | q / quaternary / 2bit |
81 | unoctogesimal |
| 5 | quinary / pental |
85 | pentoctogesimal |
| 6 | senary / heximal / seximal |
89 | enneaoctogesimal |
| 7 | septenary |
90 | nonagesimal |
| 8 | o / oct / octal / 3bit |
91 | unnonagesimal |
| 9 | nonary |
92 | duononagesimal |
| 10 | d / dec / decimal / denary |
93 | trinonagesimal |
| 11 | undecimal |
94 | tetranonagesimal |
| 12 | duodecimal / dozenal / uncial |
95 | pentanonagesimal |
| 13 | tridecimal |
96 | hexanonagesimal |
| 14 | tetradecimal |
97 | septanonagesimal |
| 15 | pentadecimal |
100 | centesimal |
| 16 | h / hex / hexadecimal / sexadecimal / 4bit |
120 | centevigesimal |
| 17 | heptadecimal |
121 | centeunvigesimal |
| 18 | octodecimal |
125 | centepentavigesimal |
| 19 | enneadecimal |
128 | centeoctovigesimal / 7bit |
| 20 | vigesimal |
144 | centetetraquadragesimal |
| 21 | unvigesimal |
169 | centenovemsexagesimal |
| 22 | duovigesimal |
185 | centepentoctogesimal |
| 23 | trivigesimal |
196 | centehexanonagesimal |
| 24 | tetravigesimal |
200 | duocentesimal |
| 25 | pentavigesimal |
210 | duocentedecimal |
| 26 | hexavigesimal |
216 | duocentehexidecimal |
| 27 | heptavigesimal / septemvigesimal |
225 | duocentepentavigesimal |
| 28 | octovigesimal |
256 | duocentehexaquinquagesimal / byte / 8bit |
| 29 | enneavigesimal |
300 | trecentesimal |
| 30 | trigesimal |
360 | trecentosexagesimal |
| 31 | untrigesimal |
512 | 9bit |
| 32 | duotrigesimal / 5bit |
1024 | 10bit |
| 33 | tritrigesimal |
2048 | 11bit |
| 34 | tetratrigesimal |
4096 | 12bit |
| 35 | pentatrigesimal |
8192 | 13bit |
| 36 | t / txt / text / hexatrigesimal |
16384 | 14bit |
| 37 | heptatrigesimal |
32768 | 15bit |
| 38 | octotrigesimal |
65536 | 16bit |
| 39 | enneatrigesimal |
131072 | 17bit |
| 40 | quadragesimal |
262144 | 18bit |
| 42 | duoquadragesimal |
524288 | 19bit |
| 45 | pentaquadragesimal |
1048576 | 20bit |
| 47 | septaquadragesimal |
2097152 | 21bit |
| 48 | octoquadragesimal |
4194304 | 22bit |
| 49 | enneaquadragesimal |
8388608 | 23bit |
| 50 | quinquagesimal |
16777216 | 24bit |
| 52 | duoquinquagesimal |
33554432 | 25bit |
| 54 | tetraquinquagesimal |
67108864 | 26bit |
| 56 | hexaquinquagesimal |
134217728 | 27bit |
| 57 | heptaquinquagesimal |
268435456 | 28bit |
| 58 | octoquinquagesimal |
536870912 | 29bit |
| 60 | sexagesimal / sexagenary |
1073741824 | 30bit |
| 62 | duosexagesimal |
2147483648 | 31bit |
| 64 | tetrasexagesimal / 6bit |
4294967296 | 32bit |
click to hide table
| name | description | example |
|---|---|---|
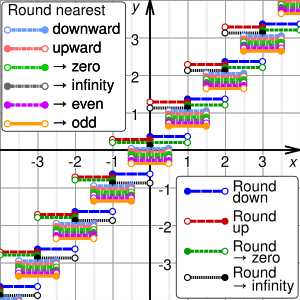
NEAR_DOWN |
round to nearest integer, towards -infinity |
|
NEAR_UP |
round to nearest integer, towards +infinity |
|
NEAR_ZERO |
round to nearest integer, towards zero |
|
NEAR_INF |
round to nearest integer, away from zero |
|
NEAR_EVEN |
round to nearest even integer |
|
NEAR_ODD |
round to nearest odd integer |
|
FLOOR |
round down (towards -infinity) |
|
CEIL |
round up (towards +infinity) |
|
TRUNC |
round down (towards zero) |
|
RAISE |
round up (away from zero) |
|
click to hide table
| name | description |
|---|---|
ROUND_NEAR_DOWN |
division rounded towards -infinity |
ROUND_NEAR_UP |
division rounded towards +infinity |
ROUND_NEAR_ZERO |
division rounded towards zero |
ROUND_NEAR_INF |
division rounded away from zero |
ROUND_NEAR_EVEN |
division rounded to nearest even integer |
ROUND_NEAR_ODD |
division rounded to nearest odd integer |
FLOOR |
floored division (towards -infinity) |
CEIL |
ceiled division (towards +infinity) |
TRUNC |
truncated division (towards zero) |
RAISE |
raised division (away from zero) |
EUCLID |
euclidean division (positive remainder) |
click to show table
| trunc | floor | euclid | round | ceil | raise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trunc | floor | euclid | round | ceil | raise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trunc | floor | euclid | round | ceil | raise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trunc | floor | euclid | round | ceil | raise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trunc | floor | euclid | round | ceil | raise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
more details/documentation in the file itself via js-docs (/** */) and additional commenting with //~
WIP
idea: BigInt >> Fraction & Infinity >> ComplexNumber
some useful math functions
also see
other-projects/useful.js
- [functions]
mapRange - [functions]
toPercent - [functions]
deg2rad - [functions]
rad2deg - [functions]
gcd - [functions]
dec2frac - [functions]
padNum - [functions]
euclideanModulo - [functions]
randomRange - [functions]
randomRangeInt - [functions]
divisionWithRest - [functions]
randomBools - [functions]
rangeGenerator - [functions]
rng32bit - [functions]
valueNoise - [functions]
sinAprx - [functions]
factorial
translate the given number to another range
function mapRange(n: number, x: number, y: number, x2: number, y2: number, limit?: boolean | undefined): number
mapRange(0.5, 0, 1, 0, 100); //=> 50
mapRange(3, 0, 1, 0, 100); //=> 300
mapRange(3, 0, 1, 0, 100, true); //=> 100calculates the percentage of the given number within the given range
function toPercent(n: number, x: number, y: number): number
toPercent(150, 100, 200); //=> 0.5 = 50%converts the given angle from DEG to RAD
function deg2rad(deg: number): numberconverts the given angle from RAD to DEG
function rad2deg(rad: number): numbercalculates the greatest common divisor of A and B (integers)
function gcd(A: number, B: number): number
gcd(45, 100); //=> 5 → (45/5)/(100/5) → 9/20converts a decimal number to an improper-fraction (rough estimation)
function dec2frac(dec: number, loop_last?: number | undefined, max_den?: number | undefined, max_iter?: number | undefined): Readonly<{
a: number;
b: number;
c: number;
i: number;
r: string;
}>
dec2frac(0.12, 2); //=> { a:0, b:4, c:33, i:0, r:"precision" } → 0+4/33 → 0.121212121212...convert number to string with padding
format: [sign] [padded start ' '] [.] [padded end '0'] [e ~]
function padNum(n: number | string, first?: number | undefined, last?: number | undefined): string
padNum("1.23e2", 3, 5); //=> "+ 1.23000e2"calculates the modulo of two whole numbers (euclidean division)
function euclideanModulo(a: number, b: number): numbergenarates a random number within given range (inclusive)
gets a random number via Math.random() and assumes that this number is in range [0 to (1 - Number.EPSILON)] (inclusive)
function randomRange(min: number, max: number): numbergenarates a random integer within given range (inclusive)
function randomRangeInt(min: number, max: number): numberdivision with two unsigned numbers
function divisionWithRest(A: number, B: number): readonly [number, number]
divisionWithRest(5, 3); //=> [1, 2] → 1+2/3also see Math-Js/BigIntType.js : #calcDivRest for a solution with arbitrary-length-integers
generate a set amount of random booleans
generator function
function randomBools(amount?: number | undefined): Generator<boolean, any, unknown>
for(const rng of randomBools(3))console.log("%O",rng);creates a generator for given range - iterable
use Array.from() to create a normal number[] array
function rangeGenerator(start: number, end: number, step?: number | undefined, overflow?: boolean | undefined): Generator<number, void, unknown>
for(const odd of rangeGenerator(1, 100, 2))console.log(odd); //~ 1 3 5 .. 97 99get a function to get random numbers like Math.random but from a given seed
uses MurmurHash3 for seeding and sfc32 for generating 32bit values
function rng32bit(seed?: string | undefined): () => number
rng32bit("seed")(); //=> 3595049765 [0 to 0xFFFFFFFF inclusive]
rng32bit("seed")()/0xFFFFFFFF; //=> 0.8370377509475307 [0.0 to 1.0 inclusive]
rng32bit("seed")()/0x100000000;//=> 0.8370377507526428 [0.0 inclusive to 1.0 exclusive]calculates value noise for given coordinates
uses quintic interpolation for mixing numbers, and a quick (non-cryptographic) hash function to get random noise from coordinates
the output is allways the same for the same input
function valueNoise(x: number, y: number): numberI used the following code to render the background on the preview of my r/place overlay script
const size = Object.freeze([1920, 1080]),
exampleNoise = new ImageData(...size, {colorSpace: "srgb"});
for(let x = 0, y = 0; y < size[1] && x < size[0]; ++x >= size[0] ? (x = 0, y++) : 0){
const pixel = valueNoise(x * 0.008, y * 0.008) * 127
+ valueNoise(x * 0.016, y * 0.016) * 63.5
+ valueNoise(x * 0.032, y * 0.032) * 31.75
+ valueNoise(x * 0.064, y * 0.064) * 15.875
+ valueNoise(x * 0.128, y * 0.128) * 7.9375;
//// + valueNoise(x * 0.256, y * 0.256) * 3.96875
//// + valueNoise(x * 0.512, y * 0.512) * 1.984375;
exampleNoise.data.set([pixel, pixel, pixel, 0xFF], (y * size[0] + x) * 4);
}
document.body.style.backgroundImage = (() => {
"use strict";
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
canvas.width = size[0];
canvas.height = size[1];
canvas.getContext("2d")?.putImageData(exampleNoise, 0, 0);
return `url(${ canvas.toDataURL("image/png") })`;
})();approximates Math.sin()
more accurate for numbers that result in numbers closer to 0
function sinAprx(x: number): number// → at around 42'000 calls it's slightly faster that `Math.sin()` and at 10'000'000 calls it's around 8 times faster (on my machine via nodejs)
const samples = 10000000,
rngScale = 8;
const rng = new Array(samples>>>rngScale);
for(let i = 0; i < rng.length; i++) rng[i] = Math.random() < 0.5 ? -Math.random() : Math.random();
const a = performance.now();
for(let i = 0; i < samples; i++) _ = sinAprx(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER * rng[i >>> rngScale] * Math.PI);
const b = performance.now();
for(let i = 0; i < samples; i++) _ = Math.sin(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER * rng[i >>> rngScale] * Math.PI);
const c = performance.now();
console.log(
"%i samples\nAprx %f ms (%f ms each)\nSin %f ms (%f ms each)\napprox.: %f times faster",
samples, (b - a).toFixed(4), ((b - a) / samples).toFixed(4), (c - b).toFixed(4), ((c - b) / samples).toFixed(4), ((c - b) / (b - a)).toFixed(4)
);calculates the factorial of a (non-zero positive bigint) number
function factorial(n: bigint): bigintfactorial(52n); //=> 80_658_175_170_943_878_571_660_636_856_403_766_975_289_505_440_883_277_824_000_000_000_000n