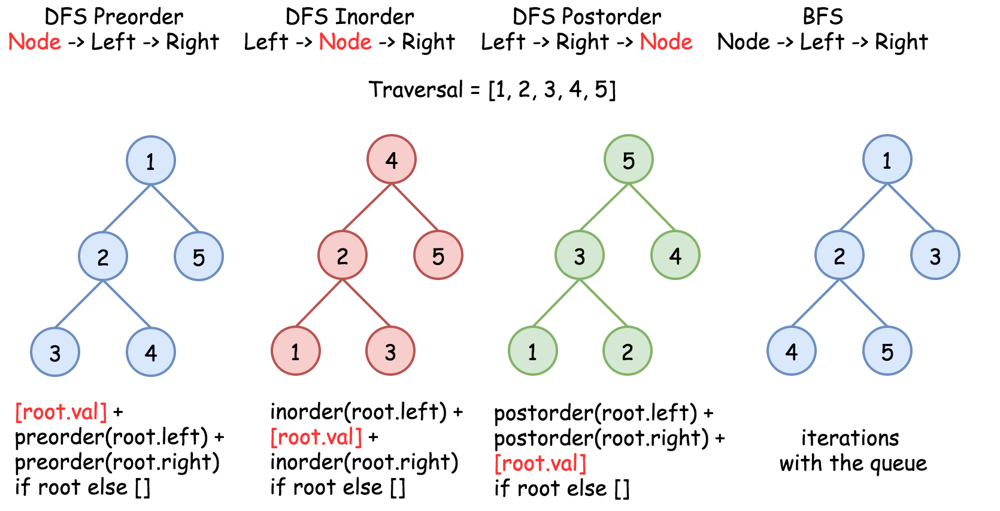
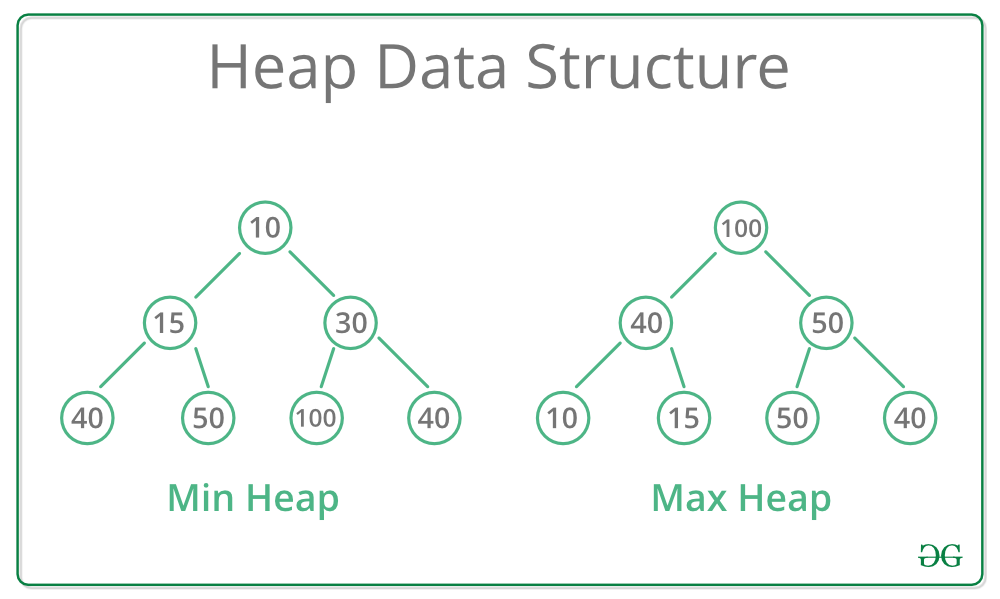
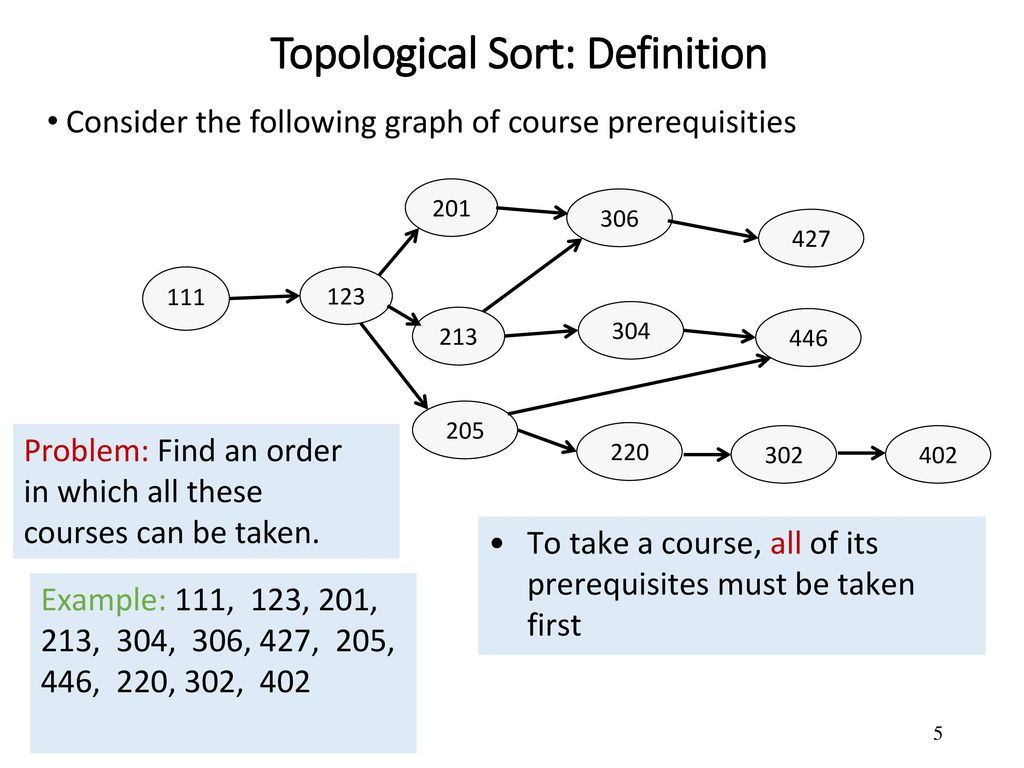
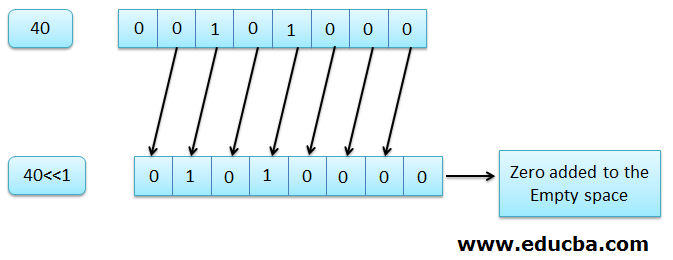
🪟 Problems
## [Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/) #3 🪟 ❓: Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters. 🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "abcabcbb" Output: 3 Explain: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3. 2️⃣ Input: s = "bbbbb" Output: 1 Explain: The answer is "b", with the length of 1. 3️⃣ Input: s = "pwwkew" Output: 3 Explain: The answer is "wke", with the length of 3. Notice that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence & not a substring. #4 Input: s = "" Output: 0
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^3) 🪐: O(min(m, n))
🐇 Solution: 🪟 Sliding Window Pattern ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function (s) {
let result = 0;
let left = 0;
let right = 0;
let set = new Set();
while (right < s.length) {
if (!set.has(s[right])) {
set.add(s[right]);
right++;
result = Math.max(result, set.size);
} else {
set.delete(s[left]);
left++;
}
}
return result;
};
❓: You are given a string s & an integer k. You can choose any character of the string & change it to any other uppercase English character. You can perform this operation at most k times.
Return the length of the longest substring containing the same letter you can get after performing the above operations.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "ABAB", k = 2 Output: 4 Explain: Replace the two 'A's with two 'B's or vice versa. 2️⃣ Input: s = "AABABBA", k = 1 Output: 4 Explain: Replace the one 'A' in the middle with 'B' & form "AABBBBA". The substring "BBBB" has the longest repeating letters, which is 4.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🪟 Sliding Window Pattern ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var characterReplacement = function (s, k) {
let left = 0;
let right = 0;
let maxCount = 0;
let map = new Map();
while (right < s.length) {
map.set(s[right], (map.get(s[right]) || 0) + 1);
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, map.get(s[right]));
if (right - left + 1 - maxCount > k) {
map.set(s[left], map.get(s[left]) - 1);
left++;
}
right++;
}
return right - left;
};
Minimum Window Substring #76 🪟
❓: Given two strings s & t of lengths m & n respectively, return the minimum window substring of s such that every character in t (including duplicates) is included in the window. If there is no such substring, return the empty string "".
The testcases will be generated such that the answer is unique.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" Output: "BANC" Explain: The minimum window substring "BANC" includes 'A', 'B', & 'C' from string t. 2️⃣ Input: s = "a", t = "a" Output: "a" 3️⃣ Input: s = "a", t = "aa" Output: "" Explain: Both 'a's from t must be included in the window. Since the largest window of s only has one 'a', return empty string.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🪟 Sliding Window Pattern ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var minWindow = function (s, t) {
let left = 0;
let right = 0;
let map = new Map();
let min = Infinity;
let result = "";
for (let i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
map.set(t[i], (map.get(t[i]) || 0) + 1);
}
let count = map.size;
while (right < s.length) {
let char = s[right];
if (map.has(char)) {
map.set(char, map.get(char) - 1);
if (map.get(char) === 0) {
count--;
}
}
right++;
while (count === 0) {
if (right - left < min) {
min = right - left;
result = s.substring(left, right);
}
let char = s[left];
if (map.has(char)) {
map.set(char, map.get(char) + 1);
if (map.get(char) > 0) {
count++;
}
}
left++;
}
}
return result;
};
|
 |
||
|
 |
||
|
 |
||
❓ # OF CONNECTED COMPONENETS IN UNDIRECTED GRAPH, FIND IF 2 NODES CONNECTED
🐣 Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph, Find whether two nodes are connected in an undirected graph, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode Union Find Algorithm Pattern ♾
⏰: O(V * logV) 🪐: O
function find(int[] parent, i) {
if (parent[i] == -1) return i;
return find(parent, parent[i]);
function union(int[] parent, x, y) {
xset = find(parent, x);
yset = find(parent, y);
parent[xset] = yset;
}
❓ MINIMUM # OF MEETINGS MAX OF INTERVALS NOT OVERLAPPING
🐣 Activity Selection Problem, Coin Change, Fractional Knapsack Problem, Job Sequencing Problem, Huffman Coding, Prim's Minimum Spanning Tree, Kruskal's Minimum Spanning Tree, Dijkstra's Shortest Path Algorithm, Bellman-Ford Algorithm, Floyd-Warshall Algorithm, Travelling Salesman Problem
🎭 PsuendoCode Greedy Pattern 💰
⏰: O(nlogn) 🪐: O(1)
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));
count = 0, end = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int[] interval : intervals) {
if (interval[0] >= end) {
count++;
end = interval[1];
}
}
return count;
❓ FIND ALL PERMUTATIONS COMBINATIONS SUBSETS PARTIONING
🐣 N-Queens Problem, Sudoku Solver, Rat in a Maze, Knight's Tour Problem, Hamiltonian Cycle, Subset Sum Problem, Permutations, Combination Sum, Palindrome Partitioning, Word Break Problem, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode Backtracking Pattern 🎲
⏰: O(n!) 🪐: O(n)
function backtrack(n, ArrayList<Integer> nums, List<List<Integer>> output, first) {
// if all integers are used up
if (first == n)
output.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(nums));
for (i = first; i < n; i++) {
// place i-th integer first
// in the current permutation
Collections.swap(nums, first, i);
// use next integers to complete the permutations
backtrack(n, nums, output, first + 1);
// backtrack
Collections.swap(nums, first, i);
}
❓ FIND OPTIMAL SOLUTION TO COMPLEX PROBLEMS MIN MAX OR COUNT OF GIVEN CONSTRAINTS
🐣 Fibonacci Numbers, House Thief, Minimum Coin Change, House Painters, Palindromic Subsequence, Longest Common Subsequence, Longest Increasing Subsequence, Longest Common Substring, Edit Distance, 0/1 Knapsack Problem, Subset Sum Problem, Unbounded Knapsack Problem, Rod Cutting, Word Break Problem, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode Dynamic Programming Pattern 📈
⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
return dp[n];
1️⃣ Bitwise XOR
❓ FIND IF NUMBER IS POWER OF 2
🐣 Power of 2, Bitwise AND of Numbers Range, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode 🧩 Bit Manipulation Pattern 🧩
⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
return (n & (n - 1)) == 0;
❓ FIND UNIQUE NUMBER IN ARRAY OF PAIRS
🐣 Single Number, Find the Missing Number, Find the Duplicate Number, Find the Corrupt Pair, etc.
2️⃣ Bitwise AND
🎭 PsuendoCode Bitwise XOR Pattern 🧩
⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
int n = nums.length;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
x1 = x1 ^ nums[i];
for (i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++)
x2 = x2 ^ i;
return x1 ^ x2;
3️⃣ Bitwise OR
❓ FIND IF NUMBER IS POWER OF 4
🐣 Power of 4, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode Bitwise OR Pattern 🧩
⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
return (n > 0) && ((n & (n - 1)) == 0) && ((n & 0xAAAAAAAA) == 0);
4️⃣ Bitwise Left Shift
❓ FIND IF NUMBER IS POWER OF 2
🐣 Power of 2, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode Bitwise Left Shift Pattern 🧩
⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
return (n > 0) && ((n & (n - 1)) == 0);
5️⃣ Bitwise Right Shift
❓ FIND IF NUMBER IS POWER OF 2
🐣 Power of 2, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode Bitwise Right Shift Pattern 🧩
⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
return (n > 0) && ((n & (n - 1)) == 0);
❓ FIND IF MATRIX IS SINGULAR
🐣 Matrix Chain Multiplication, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode 📐 Matrix Pattern 📐
⏰: O(n^3) 🪐: O(n^2)
int n = matrix.length;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (matrix[i][i] == 0) {
boolean zeroRow = true;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] != 0) {
zeroRow = false;
break;
}
}
if (zeroRow) return true;
boolean zeroColumn = true;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[j][i] != 0) {
zeroColumn = false;
break;
}
}
if (zeroColumn) return true;
}
}
return false;
❓ FIND ALL WORDS WITH GIVEN PREFIX
🐣 Word Search, Word Break Problem, etc.
🎭 PsuendoCode 📘 Trie Pattern 📘
⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
for (String word : words) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (char letter : word.toCharArray()) {
if (node.children[letter - 'a'] == null)
node.children[letter - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
node = node.children[letter - 'a'];
}
node.word = word;
}
return root;
Two Sum #1 👯
❓: Given an array of integers nums & an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
🐣: Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9, Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9, return [0, 1].
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 👯 Two Pointers ⏰: O(NlogN) 🪐: O(1)
var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
var twoSum = function(nums, target) {
let checkSum = new Map();
for(let i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
var curr = nums[i];
let diff = target-nums[i];
if(checkSum.get(diff)){
if(checkSum.get(diff)[0] === curr) {
return [checkSum.get(diff)[1], i ];
}
} else {
checkSum.set(nums[i], [diff, i]);
}
}
return checkSum
};
❓: You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock & choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
🐣: Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4], Output: 5, Explain: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) & sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5. Not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Pattern Kadane's Algorithm ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
var maxProfit = function(prices) {
let min = prices[0];
let max = 0;
for(let i=1; i<prices.length; i++){
if(prices[i] < min){
min = prices[i];
} else {
max = Math.max(max, prices[i]-min);
}
}
return max;
};
Problem : Given Arr [] of int. Return true if has duplicates :
Parameters: Ex 1: Input: nums = [1,2,3,1] Output: true. Ex 2: Input: nums = [1,2,3,4] Output: false.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 👯 Two Pointers ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
var containsDuplicate = function(nums) {
let checkSum = new Map();
for(let i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
if(checkSum.get(nums[i])){
return true;
} else {
checkSum.set(nums[i], 1);
}
}
return false;
};
var containsDuplicate = function(nums) {
return [...new Set(nums)].length !== nums.length;
};
Product of Array Except Self #238 👯
❓: Given an integer array nums, return an array answer such that answer[i] is equal to the product of all the elements of nums except nums[i].
The product of any prefix or suffix of nums is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit integer.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time & without using the division operation.
🐣: Input: nums = [1,2,3,4], Output: [24,12,8,6]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 👯 Two Pointers ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
var productExceptSelf = function(nums) {
let result = [];
let left = 1;
let right = 1;
for(let i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
result[i] = left;
left *= nums[i];
}
for(let i=nums.length-1; i>=0; i--){
result[i] *= right;
right *= nums[i];
}
return result;
};
Maximum Subarray #53 📈
❓: Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum & return its sum.
🐣: Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4], Output: 6, Explain: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Pattern Kadane's Algorithm ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
let max = nums[0];
let curr = nums[0];
for(let i=1; i<nums.length; i++){
curr = Math.max(nums[i], curr+nums[i]);
max = Math.max(max, curr);
}
return max;
};
Maximum Product Subarray #152 📈
❓: Given an integer array nums, find a contiguous non-empty subarray within the array that has the largest product, & return the product.
It is guaranteed that the answer will fit in a 32-bit integer.
A subarray is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
🐣: Input: nums = [2,3,-2,4], Output: 6, Explain: [2,3] has the largest product 6.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Pattern Kadane's Algorithm ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
var maxProduct = function(nums) {
let max = nums[0];
let min = nums[0];
let result = nums[0];
for(let i=1; i<nums.length; i++){
let temp = max;
max = Math.max(nums[i], Math.max(max*nums[i], min*nums[i]));
min = Math.min(nums[i], Math.min(temp*nums[i], min*nums[i]));
result = Math.max(result, max);
}
return result;
};
❓: Suppose an array of length n sorted in ascending order is rotated between 1 & n times. For example, the array nums = [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become:
[4,5,6,7,0,1,2] if it was rotated 4 times.
[0,1,2,4,5,6,7] if it was rotated 7 times.
Notice that rotating an array [a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-1]] 1 time results in the array [a[n-1], a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-2]].
Given the sorted rotated array nums of unique elements, return the minimum element of this array.
🐣: Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,2], Output: 1
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search Pattern ⏰: O(logN) 🪐: O(1)
Pattern: 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search
var findMin = function(nums) {
let left = 0;
let right = nums.length-1;
while(left < right){
let mid = Math.floor((left+right)/2);
if(nums[mid] > nums[right]){
left = mid+1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return nums[left];
};
❓: Suppose an array of length n sorted in ascending order is rotated between 1 & n times. For example, the array nums = [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become:
[4,5,6,7,0,1,2] if it was rotated 4 times.
[0,1,2,4,5,6,7] if it was rotated 7 times.
Notice that rotating an array [a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-1]] 1 time results in the array [a[n-1], a[0], a[1], a[2], ..., a[n-2]].
Given the sorted rotated array nums of unique elements, return the minimum element of this array.
🐣: Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,2], Output: 1
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search ⏰: O(logN) 🪐: O(1)
var findMin = function(nums) {
let left = 0;
let right = nums.length-1;
while(left < right){
let mid = Math.floor((left+right)/2);
if(nums[mid] > nums[right]){
left = mid+1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return nums[left];
};
❓: You are given an integer array nums sorted in ascending order, & an integer target.
Suppose that nums is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforeh& (i.e., [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).
If target is found in the array return its index, otherwise, return -1.
🐣: Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0, Output: 4
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search ⏰: O(logn) 🪐: O(1)
var search = function(nums, target) {
let left = 0;
let right = nums.length-1;
while(left <= right){
let mid = Math.floor((left+right)/2);
if(nums[mid] === target){
return mid;
} else if(nums[mid] >= nums[left]){
if(target >= nums[left] && target < nums[mid]){
right = mid-1;
} else {
left = mid+1;
}
} else {
if(target > nums[mid] && target <= nums[right]){
left = mid+1;
} else {
right = mid-1;
}
}
}
return -1;
};
3Sum #15 👯
❓: Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] such that i != j, i != k, & j != k, & nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0.
Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
🐣: Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4], Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N^3) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 👯 Two Pointers ⏰: O(N^2) 🪐: O(N)
var threeSum = function(nums) {
let result = [];
nums.sort((a,b) => a-b);
for(let i=0; i<nums.length-2; i++){
if(i > 0 && nums[i] === nums[i-1]) continue;
let left = i+1;
let right = nums.length-1;
while(left < right){
let sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum === 0){
result.push([nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]]);
while(left < right && nums[left] === nums[left+1]) left++;
while(left < right && nums[right] === nums[right-1]) right--;
left++;
right--;
} else if(sum < 0){
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
};
❓: Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a poat coordinate (i, ai) n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of the line i is at (i, ai) & (i, 0) Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water
Notice that you may not slant the container.
🐣: Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7], Output: 49
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 👯 Two Pointers ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var maxArea = function(height) {
let left = 0;
let right = height.length-1;
let max = 0;
while(left < right){
let area = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right-left);
max = Math.max(max, area);
if(height[left] < height[right]){
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
return max;
};
❓: Given two integers a & b, return sum of the two integers without using the operators + & -.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: a = 1, b = 2. Output: 3 2️⃣ Input: a = 2, b = 3 Output: 5.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
var getSum = function(a, b) {
let carry; // store carry
while(a!==0){
carry = a & b;
b = a ^ b;
a = carry << 1;
}
return b
};
Divide Two Integers #29 🧩
❓: Given two integers dividend & divisor, divide two integers without using multiplication, division, & mod operator.
Return the quotient after dividing dividend by divisor.
The integer division should truncate toward zero, which means losing its fractional part. For example, truncate(8.345) = 8 & truncate(-2.7335) = -2.
Note: Assume we are dealing with an environment that could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−231, 231 − 1]. For this problem, assume that your function returns 231 − 1 when the division result overflows.
🐣: Input: dividend = 10, divisor = 3, Output: 3
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(logn) 🪐: O(logn)
var divide = function(dividend, divisor) {
if (dividend === 0 || divisor === 0) return 0
let isNegative = false;
let quotient = 0;
if ((divisor < 0 || dividend < 0) && !(divisor < 0 && dividend < 0)) isNegative = true;
dividend = Math.abs(dividend)
divisor = Math.abs(divisor)
while (dividend >= divisor) {
let carry = 1, tempDividend= dividend, tempDivisor = divisor
while (tempDivisor <= (tempDividend>> 1)){
carry <<= 1
tempDividend>>= 1
tempDivisor <<= 1
}
quotient += carry
dividend -= tempDivisor
}
if (isNegative) return -quotient
if (quotient >= 2**31) {
return 2**31 - 1
}
return quotient
};
Number of 1 Bits #191 🧩
❓: Write a function that takes an unsigned integer & returns the number of '1' bits it has (aka Hamming weight).
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011 Output: 3 . N as a total of three '1' bits.2️⃣ Input: n = 00000000000000000000000010000000 Output: 1 3️⃣ Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101 Output: 31
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
var hammingWeight = function(n) {
let count = 0;
while(n!=0){
n = n&(n-1); //mask<<1
count++;
}
return count
};
Counting Bits #338 🧩
❓: Given an integer n, return an array ans of length n + 1 such that for each i (0 <= i <= n), ans[i] is the number of 1's in the binary representation of i.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: n = 2 Output: [0,1,1] Explain: 0 --> 0 1 --> 1 2 --> 10 2️⃣ Input: n = 5 Output: [0,1,1,2,1,2]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
var countBits = function(n) {
let result = [0];
for(let i = 1; i <= n; i++){
result.push(result[i>>1] + (i&1));
}
return result;
};
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(N)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
const countBits = (n) => {
const res = new Array(n);
res[0] = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i % 2 === 0) res[i] = res[i / 2];
else res[i] = res[i - 1] + 1;
}
return res;
};
Missing Number #268 🧩
❓: Given an [] containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only num in the range tht missing from the []
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [3,0,1] Output: 2 Explain: n = 3 since there are 3 num, so all n are in range [0,3]. 2 is the missing num in the range it does not appear in nums. 2️⃣ Input: nums = [0,1] Output: 2 3️⃣ Input: nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1] Output: 8
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(N)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var missingNumber = function (nums) {
let i = 0;
let temp = 0;
while (i < nums.length) {
if (nums[i] != i && nums.length > nums[i]) {
temp = nums[nums[i]];
nums[nums[i]] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
} else {
i++;
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i != nums[i]) return i;
}
return nums.length;
};
Reverse Bits #190 🧩
❓: Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: n = 00000010100101000001111010011100 Output: 964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
Explain: The input binary string 00000010100101000001111010011100 represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is 00111001011110000010100101000000. 2️⃣ Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
Output: 3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111)
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(N) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 🧩 Bit Manipulation ⏰: O(1) 🪐: O(1)
var reverseBits = function (n) {
var len = 32;
var arr = new Array();
while (len > 0) {
var t = n & 1;
n = n >> 1;
arr.push(t);
len--;
}
var res = arr.join("");
return parseInt(res, 2);
};
Climbing Stairs #70 📈
❓: You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top. Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: n = 2 Output: 2. Explain: There are two ways to climb to the top. 1. 1 step + 1 step 2. 2 steps
2️⃣ Input: n = 3 Output: 3. Explain: There are three ways to climb to the top. 1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step 2. 1 step + 2 steps 3. 2 steps + 1 step
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var climbStairs = function (n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
let dp = new Array(n + 1); // ways to climb array
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) { //Either climb 1 stair & then climb the rest i-1 stairs X ways.
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]; //- Or climb 2 stairs at once & then climb the rest i-2 stairs Y ways.
} //Total: X + Y ways
return dp[n];
};
Coin Change #322 📈
❓: You are given an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations & an integer amount representing a total amount of money. Return the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: coins = [1,2,5], amount = 11 Output: 3 Explain: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
2️⃣ Input: coins = [2], amount = 3 Output: -1
3️⃣ Input: coins = [1], amount = 0 Output: 0
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^amount) 🪐: O(amount)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n^amount) 🪐: O(n^amount)
var coinChange = function (coins, amount) {
let dp = new Array(amount + 1).fill(amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
if (coins[j] <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
};
❓: Given an integer array nums, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] Output: 4 Explain: The longest increasing subsequence is [2,3,7,101], therefore the length is 4. 2️⃣ Input: nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3] Output: 4 3️⃣ Input: nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7] Output: 1
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(n^2)
var lengthOfLIS = function (nums) {
let dp = new Array(nums.length).fill(1);
let max = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
}
}
return max;
};
Longest Common Subsequence #1143 📈
❓: Given two strings text1 & text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence. If there is no common subsequence, return 0. A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters(can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters. (eg, "ace" is a subsequence of "abcde" while "aec" is not). A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" Output: 3 Explain: The longest common subsequence is "ace" & its length is 3. 2️⃣ Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc" Output: 3 3️⃣ Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "def" Output: 0
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(m*n) 🪐: O(m*n)
var longestCommonSubsequence = function (text1, text2) {
let dp = new Array(text1.length + 1)
.fill(0)
.map(() => new Array(text2.length + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= text1.length; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= text2.length; j++) {
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[text1.length][text2.length];
};
❓: Given a string s & a dictionary of strings wordDict, return true if s can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words. Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet","code"] Output: true Explain: Return true because "leetcode" can be segmented as "leet code". 2️⃣ Input: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple","pen"] Output: true Explain: Return true because "applepenapple" can be segmented as "apple pen apple". Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word. 3️⃣ Input: s = "cats&og", wordDict = ["cats","dog","s&","&","cat"] Output: false
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(n^2)
var wordBreak = function (s, wordDict) {
let dp = new Array(s.length + 1).fill(false);
dp[0] = true;
for (let i = 1; i <= s.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (dp[j] && wordDict.includes(s.substring(j, i))) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length];
};
Combination Sum #377 📈
❓: Given an integer array with all positive numbers & no duplicates, find the number of possible combinations that add up to a positive integer target.
🐣: Input: nums = [1, 2, 3] target = 4 Output: 7 Explain: The possible combination ways are: (1, 1, 1, 1) (1, 1, 2) (1, 2, 1) (1, 3) (2, 1, 1) (2, 2) (3, 1) Note that different sequences are counted as different combinations. Therefore the output is 7.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n*target) 🪐: O(n*target)
var combinationSum4 = function (nums, target) {
let dp = new Array(target + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (let i = 1; i <= target; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] <= i) {
dp[i] += dp[i - nums[j]];
}
}
}
return dp[target];
};
House Robber #198
❓: You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constrastopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security system connected & it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night. Given an integer array nums representing the amount of money of each house, return the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [1,2,3,1] Output: 4 Explain: Rob house 1 (money = 1) & then rob house 3 (money = 3). Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4. 2️⃣ Input: nums = [2,7,9,3,1] Output: 12 Explain: Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) & rob house 5 (money = 1). Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var rob = function (nums) {
let dp = new Array(nums.length + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = nums[0];
for (let i = 2; i <= nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i - 1]);
}
return dp[nums.length];
};
House Robber II #213
❓: You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed. All houses at this place are arranged in a circle. That means the first house is the neighbor of the last one. Meanwhile, adjacent houses have security system connected & it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night. Given an integer array nums representing the amount of money of each house, return the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [2,3,2] Output: 3 Explain: You cannot rob house 1 (money = 2) & then rob house 3 (money = 2), because they are adjacent houses. 2️⃣ Input: nums = [1,2,3,1] Output: 4 Explain: Rob house 1 (money = 1) & then rob house 3 (money = 3). Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4. 3️⃣ Input: nums = [0] Output: 0
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var rob = function (nums) {
if (nums.length == 1) return nums[0];
return Math.max(
robRange(nums, 0, nums.length - 2),
robRange(nums, 1, nums.length - 1)
);
};
var robRange = function (nums, start, end) {
let dp = new Array(nums.length + 1).fill(0);
dp[start] = nums[start];
dp[start + 1] = Math.max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]);
for (let i = start + 2; i <= end; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2] + nums[i]);
}
return dp[end];
};
Decode Ways #91 📈
❓: A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping: 'A' -> 1 'B' -> 2 ... 'Z' -> 26 Given a non-empty string s containing only digits, determine the total number of ways to decode it. The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit integer.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "12" Output: 2 Explain: It could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12). 2️⃣ Input: s = "226" Output: 3 Explain: It could be decoded as "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), or "BBF" (2 2 6). 3️⃣ Input: s = "0" Output: 0 Explain: There is no character that is mapped to a number starting with 0. The only valid mappings with 0 are 'J' -> "10" & 'T' -> "20", neither of which start with 0. Hence, there are no valid ways to decode this since all digits need to be mapped. #4 Input: s = "1" Output: 1
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var numDecodings = function (s) {
if (s[0] == "0") return 0;
let dp = new Array(s.length + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= s.length; i++) {
let first = parseInt(s.substring(i - 1, i));
let second = parseInt(s.substring(i - 2, i));
if (first >= 1 && first <= 9) {
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
}
if (second >= 10 && second <= 26) {
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
return dp[s.length];
};
Unique Paths #62 📈
❓: A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below). The robot can only move either down or right at any poin time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below). How many possible unique paths are there?
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: m = 3, n = 7 Output: 28 2️⃣ Input: m = 3, n = 2 Output: 3 Explain: From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner: 1. Right -> Down -> Down 2. Down -> Down -> Right 3. Down -> Right -> Down 3️⃣ Input: m = 7, n = 3 Output: 28 #4 Input: m = 3, n = 3 Output: 6
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Memoization ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var uniquePaths = function (m, n) {
let dp = new Array(m).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
for (let i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
};
Jump Game #55 📈
❓: Given an array of non-negative integers nums, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array. Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position. Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4] Output: true Explain: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index. 2️⃣ Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4] Output: false Explain: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(2^n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming Tabulation ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var canJump = function (nums) {
let dp = new Array(nums.length).fill(false);
dp[0] = true;
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (dp[j] && j + nums[j] >= i) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[nums.length - 1];
};
Clone Graph #133 🌳
❓: Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph. Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a val (int) & a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explain: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 2️⃣ Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] 3️⃣ Input: adjList = [] Output: [] #4 Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌳 BFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var cloneGraph = function (node) {
if (!node) return node;
let map = new Map();
let clone = new Node(node.val, []);
map.set(node, clone);
let queue = [node];
while (queue.length) {
let n = queue.shift();
for (let neighbor of n.neighbors) {
if (!map.has(neighbor)) {
map.set(neighbor, new Node(neighbor.val, []));
queue.push(neighbor);
}
map.get(n).neighbors.push(map.get(neighbor));
}
}
return clone;
};
Course Schedule #207 📅
❓: There are a total of numCourses courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to numCourses - 1. You are given an array prerequisites where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you must take course bi first if you want to take course ai. For example, the pair [0, 1], indicates that to take course 0 you have to first take course 1. Return true if you can finish all courses. Otherwise, return false.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] Output: true Explain: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible. 2️⃣ Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: false Explain: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, & to take course 0 you should also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📅 Topological Sort ⏰: O(V+E) 🪐: O(V+E)
var canFinish = function (numCourses, prerequisites) {
let graph = new Map();
let indegree = new Array(numCourses).fill(0);
for (let [course, pre] of prerequisites) {
if (!graph.has(pre)) graph.set(pre, []);
graph.get(pre).push(course);
indegree[course]++;
}
let queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < indegree.length; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) queue.push(i);
}
let count = 0;
while (queue.length) {
let course = queue.shift();
count++;
if (graph.has(course)) {
for (let next of graph.get(course)) {
indegree[next]--;
if (indegree[next] == 0) queue.push(next);
}
}
}
return count == numCourses;
};
Pacific Atlantic Water Flow #417 🌳
❓: Given an m x n matrix of non-negative integers representing the height of each unit cell in a continent, the "Pacific ocean" touches the left & top edges of the matrix & the "Atlantic ocean" touches the right & bottom edges. Water can only flow in four directions (up, down, left, or right) from a cell to another one with height equal or lower. Find the list of grid coordinates where water can flow to both the Pacific & Atlantic ocean.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]] Output: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]] Explain: Pacific ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 1 2 2 3 (5) ~ 3 2 3 (4) (4) ~ 2 4 (5) 3 1 ~ (6) (7) 1 4 5 ~ (5) 1 1 2 4 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ Atlantic 2️⃣ Input: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]] Output: [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌳 BFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var pacificAtlantic = function (heights) {
let m = heights.length;
let n = heights[0].length;
let pacific = new Array(m).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(false));
let atlantic = new Array(m).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(false));
let queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
queue.push([i, 0]);
pacific[i][0] = true;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.push([0, i]);
pacific[0][i] = true;
}
🌳 BFS(heights, pacific, queue);
queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
queue.push([i, n - 1]);
atlantic[i][n - 1] = true;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.push([m - 1, i]);
atlantic[m - 1][i] = true;
}
🌳 BFS(heights, atlantic, queue);
let res = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) res.push([i, j]);
}
}
return res;
};
function 🌳 BFS(heights, ocean, queue) {
let dirs = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]];
while (queue.length) {
let [i, j] = queue.shift();
for (let dir of dirs) {
let x = i + dir[0];
let y = j + dir[1];
if (
x >= 0 &&
x < heights.length &&
y >= 0 &&
y < heights[0].length &&
!ocean[x][y]
) {
if (heights[x][y] >= heights[i][j]) {
ocean[x][y] = true;
queue.push([x, y]);
}
}
}
}
}
Number of Islands #200 🌳
Pattern Used: 🌳 BFS Pattern 🌲 DFS Pattern Union Find Pattern
❓: Given an m x n 2d grid map of '1's (l&) & '0's (water), return the number of islands. An isl& is surrounded by water & is formed by connecting adjacent l&s horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: grid = [ ["1","1","1","1","0"], ["1","1","0","1","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","0","0","0"] ] Output: 1 2️⃣ Input: grid = [ ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","1","0","0"], ["0","0","0","1","1"] ] Output: 3
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌳 BFS ⏰: O(mn) 🪐: O(mn)
var numIslands = function (grid) {
let m = grid.length;
let n = grid[0].length;
let count = 0;
let dirs = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == "1") {
count++;
grid[i][j] = "0";
let queue = [[i, j]];
while (queue.length) {
let [x, y] = queue.shift();
for (let dir of dirs) {
let a = x + dir[0];
let b = y + dir[1];
if (
a >= 0 &&
a < m &&
b >= 0 &&
b < n &&
grid[a][b] == "1"
) {
grid[a][b] = "0";
queue.push([a, b]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return count;
};
Longest Consecutive Sequence #128 ♾
❓: Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence. You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2] Output: 4 Explain: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4. 2️⃣ Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] Output: 9
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: ♾ Union Find ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var longestConsecutive = function (nums) {
let set = new Set(nums);
let max = 0;
for (let num of set) {
if (!set.has(num - 1)) {
let curr = num;
let count = 1;
while (set.has(curr + 1)) {
curr++;
count++;
}
max = Math.max(max, count);
}
}
return max;
};
Insert Interval #57 🚗🚙
❓: Given a set of non-overlapping intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals (merge if necessary). You may assume that the intervals were initially sorted according to their start times.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5] Output: [[1,5],[6,9]] 2️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8] Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]] Explain: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🚗🚙 Merge Intervals ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var insert = function (intervals, newInterval) {
let res = [];
let i = 0;
while (i < intervals.length && intervals[i][1] < newInterval[0]) {
res.push(intervals[i]);
i++;
}
while (i < intervals.length && intervals[i][0] <= newInterval[1]) {
newInterval[0] = Math.min(newInterval[0], intervals[i][0]);
newInterval[1] = Math.max(newInterval[1], intervals[i][1]);
i++;
}
res.push(newInterval);
while (i < intervals.length) {
res.push(intervals[i]);
i++;
}
return res;
};
Merge Intervals #56 🚗🚙 💰
❓: Given an array of intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], merge all overlapping intervals, & return an array of the non-overlapping intervals that cover all the intervals in the input.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] Explain: Since intervals [1,3] & [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6]. 2️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]] Output: [[1,5]] Explain: Intervals [1,4] & [4,5] are considered overlapping.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🚗🚙 Merge Intervals ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var merge = function (intervals) {
if (intervals.length <= 1) return intervals;
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
let res = [intervals[0]];
for (let i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
let curr = intervals[i];
let prev = res[res.length - 1];
if (curr[0] <= prev[1]) {
prev[1] = Math.max(prev[1], curr[1]);
} else {
res.push(curr);
}
}
return res;
};
Non-overlapping Intervals #435 🚗🚙
❓: Given an array of intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], return the minimum number of intervals you need to remove to make the rest of the intervals non-overlapping.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,3]] Output: 1 Explain: [1,3] can be removed & the rest of the intervals are non-overlapping. 2️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,2],[1,2],[1,2]] Output: 2 Explain: You need to remove two [1,2] to make the rest of the intervals non-overlapping. 3️⃣ Input: intervals = [[1,2],[2,3]] Output: 0 Explain: You don't need to remove any of the intervals since they're already non-overlapping.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🚗🚙 Merge Intervals ⏰: O(nlogn) 🪐: O(1)
var eraseOverlapIntervals = function (intervals) {
if (intervals.length <= 1) return 0;
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[1] - b[1]);
let count = 0;
let prev = intervals[0];
for (let i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
let curr = intervals[i];
if (curr[0] < prev[1]) {
count++;
} else {
prev = curr;
}
}
return count;
};
Reverse a Linked List #206 🐰&🐢
❓: Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, & return the reversed list.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [5,4,3,2,1] 2️⃣ Input: head = [1,2] Output: [2,1] 3️⃣ Input: head = [] Output: []
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰:
🐇 Solution: 🐰&🐢 Fast & Slow Pointers ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var reverseList = function (head) {
let prev = null;
let curr = head;
while (curr) {
let next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
};
which algorithm from ./algorithms.md is used in this solution?
the
Detect Cycle in a Linked List #141 🐰&🐢
❓: Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it. There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter. Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 Output: true Explain: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed). 2️⃣ Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0 Output: true Explain: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node. 3️⃣ Input: head = [1], pos = -1 Output: false Explain: There is no cycle in the linked list.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🐰&🐢 Fast & Slow Pointers ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var hasCycle = function (head) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) return true;
}
return false;
};
Merge Two Sorted Lists #21 🐰&🐢
❓: Merge two sorted linked lists & return it as a sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4] 2️⃣ Input: l1 = [], l2 = [] Output: [] 3️⃣ Input: l1 = [], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🐰&🐢 Fast & Slow Pointers ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) {
let dummy = new ListNode();
let curr = dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
curr.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
curr.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
if (l1) curr.next = l1;
if (l2) curr.next = l2;
return dummy.next;
};
Pattern Used: K MERGE
❓: You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order. Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list & return it.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 2️⃣ Input: lists = [] Output: [] 3️⃣ Input: lists = [[]] Output: []
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: Heap ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
import ListNode from "DataStructures/LinkedList/ListNode.js";
import MinHeap from "DataStructures/Heaps/MinHeap.js";
const mergeKLists = function (lists) {
if (lists.length === 0) return null;
let dummy = new ListNode();
let curr = dummy;
let minHeap = new MinHeap();
for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
if (lists[i]) minHeap.insert(lists[i]);
}
while (minHeap.size() > 0) {
let node = minHeap.remove();
curr.next = node;
curr = curr.next;
if (node.next) minHeap.insert(node.next);
}
return dummy.next;
};
Remove Nth Node From End Of List #19 🐰&🐢
❓: Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list & return its head.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 Output: [1,2,3,5] 2️⃣ Input: head = [1], n = 1 Output: [] 3️⃣ Input: head = [1,2], n = 1 Output: [1]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🐰&🐢 Fast & Slow Pointers Fast & Slow Pointers ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
let dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
let slow = dummy;
let fast = dummy;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
};
Reorder List #143 🐰&🐢
❓: Given the head of a singly linked list, reorder the list to be: head -> node 2 -> node 3 -> node 4 -> ... -> node n -> null. You may not modify the values in the list's nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: head = [1,2,3,4] Output: [1,4,2,3] 2️⃣ Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [1,5,2,4,3]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🐰&🐢 Fast & Slow Pointers ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var reorderList = function (head) {
if (!head) return null;
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
let prev = null;
let curr = slow;
while (curr) {
let next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
let first = head;
let second = prev;
while (second.next) {
let temp = first.next;
first.next = second;
first = temp;
temp = second.next;
second.next = first;
second = temp;
}
};
Set Matrix Zeroes #73 📐
❓: Given an m x n matrix. If an element is 0, set its entire row & column to 0. Do it in-place.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] Output: [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]] 2️⃣ Input: matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]] Output: [[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(mn) 🪐: O(m+n)
🐇 Solution: 📐 Matrix Pattern ⏰: O(mn) 🪐: O(1)
var setZeroes = function (matrix) {
let rows = new Set();
let cols = new Set();
for (let i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] === 0) {
rows.add(i);
cols.add(j);
}
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (rows.has(i) || cols.has(j)) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
};
Spiral Matrix #54 📐
Pattern Used: 📐 Matrix Pattern
❓: Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5] 2️⃣ Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(mn) 🪐: O(mn)
🐇 Solution: 📐 Matrix Pattern ⏰: O(mn) 🪐: O(mn)
var spiralOrder = function (matrix) {
let result = [];
let top = 0;
let bottom = matrix.length - 1;
let left = 0;
let right = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (top <= bottom && left <= right) {
for (let i = left; i <= right; i++) {
result.push(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
for (let i = top; i <= bottom; i++) {
result.push(matrix[i][right]);
}
right--;
if (top <= bottom) {
for (let i = right; i >= left; i--) {
result.push(matrix[bottom][i]);
}
bottom--;
}
if (left <= right) {
for (let i = bottom; i >= top; i--) {
result.push(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
}
return result;
};
Rotate Image #48 📐
Pattern Used: 📐 Matrix Pattern
❓: You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image, rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]] 2️⃣ Input: matrix = [[5,1,9,11],[2,4,8,10],[13,3,6,7],[15,14,12,16]] Output: [[15,13,2,5],[14,3,4,1],[12,6,8,9],[16,7,10,11]]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰:
🐇 Solution: MatrixPattern ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(1)
var rotate = function (matrix) {
let n = matrix.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
for (let j = i; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - j - 1][i];
matrix[n - j - 1][i] = matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1];
matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1] = matrix[j][n - i - 1];
matrix[j][n - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
};
Word Search #79 📐
Pattern Used: Backtracking 📐 Matrix Pattern
❓: Given an m x n grid of characters board & a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" Output: true 2️⃣ Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" Output: true 3️⃣ Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" Output: false
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰ O(mn * 4^L) 🪐: O(mn)
🐇 Solution: MatrixPattern ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var exist = function (board, word) {
let m = board.length;
let n = board[0].length;
let visited = new Array(m);
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
visited[i] = new Array(n).fill(false);
}
let 🌲 DFS = (i, j, k) => {
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || visited[i][j] || board[i][j] !== word[k]) {
return false;
}
if (k === word.length - 1) {
return true;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
let result =
🌲 DFS(i + 1, j, k + 1) ||
🌲 DFS(i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
🌲 DFS(i, j + 1, k + 1) ||
🌲 DFS(i, j - 1, k + 1);
visited[i][j] = false;
return result;
};
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (🌲 DFS(i, j, 0)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
};
Valid Anagram #242
❓: Given two strings s & t , write a function to determine if t is an anagram of s.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" Output: true 2️⃣ Input: s = "rat", t = "car" Output: false
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(nlogn) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: Hash Table ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var isAnagram = function (s, t) {
if (s.length !== t.length) {
return false;
}
let map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
map.set(s[i], (map.get(s[i]) || 0) + 1);
}
for (let i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
if (!map.has(t[i])) {
return false;
}
map.set(t[i], map.get(t[i]) - 1);
if (map.get(t[i]) < 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
Group Anagrams #49
❓: Given an array of strings strs, group the anagrams together. You can return the answer in any order.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: strs = ["eat","tea","tan","ate","nat","bat"] Output: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]] 2️⃣ Input: strs = [""] Output: [[""]] 3️⃣ Input: strs = ["a"] Output: [["a"]]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^2)
🐇 Solution: Hash Table ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var groupAnagrams = function (strs) {
let map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
let sorted = strs[i].split("").sort().join("");
if (!map.has(sorted)) {
map.set(sorted, []);
}
map.get(sorted).push(strs[i]);
}
return [...map.values()];
};
Pattern Used: Stack
❓: Given a string s containing just the characters '(', ')', '{', '}', '[' & ']', determine if the input string is valid.
An input string is valid if:
Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "()" Output: true 2️⃣ Input: s = "()[]{}" Output: true 3️⃣ Input: s = "(]" Output: false #4 Input: s = "([)]" Output: false #5 Input: s = "{[]}" Output: true
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: Stack ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var isValid = function (s) {
let stack = [];
let map = new Map();
map.set("(", ")");
map.set("{", "}");
map.set("[", "]");
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if (map.has(s[i])) {
stack.push(s[i]);
} else {
if (map.get(stack.pop()) !== s[i]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.length === 0;
};
Valid Palindrome #125 👯
❓: Given a string s, determine if it is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters & ignoring cases.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama" Output: true Explain: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome.
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰:
🐇 Solution: 👯 Two Pointers ⏰:
var isPalindrome = function(s) {
let cursor1 = 0;
let cursor2 = s.length - 1;
while (cursor1 < cursor2) {
if (!(/^[a-zA-Z0-9]*$/.test(s[cursor1]))) {
cursor1++;
continue;
}
if (!(/^[a-zA-Z0-9]*$/.test(s[cursor2]))) {
cursor2--;
continue;
}
if (s[cursor1].toLowerCase() === s[cursor2].toLowerCase()) {
cursor1++;
cursor2--;
continue;
}
return false;
}
return true;
};
}
❓: Given a string s, return the longest palindromic substring in s.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "babad" Output: "bab" Note: "aba" is also a valid answer. 2️⃣ Input: s = "cbbd" Output: "bb" 3️⃣ Input: s = "a" Output: "a" #4 Input: s = "ac" Output: "a"
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^3) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(n^2)
var longestPalindrome = function (s) {
let result = "";
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
let odd = exp&(s, i, i);
let even = exp&(s, i, i + 1);
let max = odd.length > even.length ? odd : even;
if (max.length > result.length) {
result = max;
}
}
return result;
};
function exp&(s, left, right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length && s[left] === s[right]) {
left--;
right++;
}
return s.substring(left + 1, right);
}
Palindromic Substrings #647 📈
❓: Given a string s, return the number of palindromic substrings in it.
A string is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: s = "abc" Output: 3 Explain: Three palindromic strings: "a", "b", "c". 2️⃣ Input: s = "aaa" Output: 6 Explain: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa".
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n^3) 🪐: O(1)
🐇 Solution: 📈 Dynamic Programming ⏰: O(n^2) 🪐: O(n^2)
var countSubstrings = function (s) {
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
count += exp&(s, i, i);
count += exp&(s, i, i + 1);
}
return count;
};
function exp&(s, left, right) {
let count = 0;
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length && s[left] === s[right]) {
count++;
left--;
right++;
}
return count;
}
❓: Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3 2️⃣ Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: 2 3️⃣ Input: root = [] Output: 0 #4 Input: root = [0] Output: 1
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var maxDepth = function (root) {
if (!root) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
};
Same Tree #100🌲
❓: Given the roots of two binary trees p & q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, & the nodes have the same value.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] Output: true 2️⃣ Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] Output: false 3️⃣ Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2] Output: false
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var isSameTree = function (p, q) {
if (!p && !q) return true;
if (!p || !q) return false;
if (p.val !== q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
};
Invert/Flip Binary Tree #226🌲
❓: Invert a binary tree.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1] 2️⃣ Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: [2,3,1] 3️⃣ Input: root = [] Output: []
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var invertTree = function (root) {
if (!root) return null;
let temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
};
Pattern Used: 🌲 DFS
❓: Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any path.
A path is a collection of nodes that are connected by edges, where no node is connected to more than two other nodes. The path must contain at least one node & does not need to go through the root.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 6 2️⃣ Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 42
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var maxPathSum = function (root) {
let max = -Infinity;
function 🌲 DFS(node) {
if (!node) return 0;
let left = Math.max(🌲 DFS(node.left), 0);
let right = Math.max(🌲 DFS(node.right), 0);
max = Math.max(max, left + right + node.val);
return Math.max(left, right) + node.val;
}
🌲 DFS(root);
return max;
};
Pattern Used: 🌳 BFS
❓: Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]] 2️⃣ Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]] 3️⃣ Input: root = [] Output: []
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌳 BFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var levelOrder = function (root) {
let result = [];
function 🌲 DFS(node, level) {
if (!node) return;
if (!result[level]) result[level] = [];
result[level].push(node.val);
🌲 DFS(node.left, level + 1);
🌲 DFS(node.right, level + 1);
}
🌲 DFS(root, 0);
return result;
};
❓: Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize & deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string & this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5] Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌳 BFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var serialize = function (root) {
let result = [];
function 🌲 DFS(node) {
if (!node) {
result.push(null);
return;
}
result.push(node.val);
🌲 DFS(node.left);
🌲 DFS(node.right);
}
🌲 DFS(root);
return result;
};
var deserialize = function (data) {
let index = 0;
function 🌲 DFS() {
if (index >= data.length || data[index] === null) {
index++;
return null;
}
let node = new TreeNode(data[index]);
index++;
node.left = 🌲 DFS();
node.right = 🌲 DFS();
return node;
}
return 🌲 DFS();
};
Subtree of Another Tree #572🌲
❓: Given the roots of two binary trees root & subRoot, return true if there is a subtree of root with the same structure & node values of subRoot & false otherwise.
A subtree of a binary tree tree is a tree that consists of a node in tree & all of this node's descendants. The tree tree could also be considered as a subtree of itself.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [3,4,5,1,2], subRoot = [4,1,2] Output: true 2️⃣ Input: root = [3,4,5,1,2,null,null,null,null,0], subRoot = [4,1,2] Output: false
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var isSubtree = function (root, subRoot) {
if (!root) return false;
if (isSameTree(root, subRoot)) return true;
return isSubtree(root.left, subRoot) || isSubtree(root.right, subRoot);
};
var isSameTree = function (p, q) {
if (!p && !q) return true;
if (!p || !q) return false;
if (p.val !== q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
};
❓: Given two integer arrays preorder & inorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree & inorder is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct & return the binary tree.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 2️⃣ Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] Output: [-1]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var buildTree = function (preorder, inorder) {
if (!preorder.length || !inorder.length) return null;
let root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
let index = inorder.indexOf(preorder[0]);
root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1, index + 1), inorder.slice(0, index));
root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index + 1), inorder.slice(index + 1));
return root;
};
❓: Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search tree (BST).
A valid BST is defined as follows:
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
Both the left & right subtrees must also be 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search trees.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: true 2️⃣ Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] Output: false
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var isValidBST = function (root) {
function 🌲 DFS(node, min, max) {
if (!node) return true;
if (node.val <= min || node.val >= max) return false;
return 🌲 DFS(node.left, min, node.val) && 🌲 DFS(node.right, node.val, max);
}
return 🌲 DFS(root, -Infinity, Infinity);
};
❓: Given the root of a Binary Search tree, & an integer k, return the kth (1-indexed) smallest element in the tree.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 Output: 1 2️⃣ Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3 Output: 3
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var kthSmallest = function (root, k) {
let result = [];
function 🌲 DFS(node) {
if (!node) return;
🌲 DFS(node.left);
result.push(node.val);
🌲 DFS(node.right);
}
🌲 DFS(root);
return result[k - 1];
};
❓: Given a 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: "The lowest common ancestor of two nodes p & q in a binary tree T is the lowest node that has both p & q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself)."
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 Output: 6 2️⃣ Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 Output: 2
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 🌲 DFS ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
};
❓: Implement a 📘 Trie with insert, search, & startsWith methods.
A 📘 Trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store & re📘 Trieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete & spellchecker.
Implement the 📘 Trie class: 📘 Trie() Initializes the 📘 Trie object.
void insert(String word) Inserts the string word into the 📘 Trie.
boolean search(String word) Returns true if the string word is in the 📘 Trie (i.e., was inserted before), & false otherwise.
boolean startsWith(String prefix) Returns true if there is a previously inserted string word that has the prefix prefix, & false otherwise
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: ["📘 Trie","insert","search","search","startsWith","insert","search"] Output: [null,null,true,false,true,null,true] Explain: 📘 Trie 📘 Trie = new 📘 Trie(); 📘 Trie.insert("apple"); 📘 Trie.search("apple"); // return True 📘 Trie.search("app"); // return False 📘 Trie.startsWith("app"); // return True 📘 Trie.insert("app"); 📘 Trie.search("app"); // return True
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📘 Trie ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var 📘 Trie = function () {
this.root = {};
};
📘 Trie.prototype.insert = function (word) {
let node = this.root;
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
if (!node[word[i]]) node[word[i]] = {};
node = node[word[i]];
}
node.isEnd = true;
};
📘 Trie.prototype.search = function (word) {
let node = this.root;
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
if (!node[word[i]]) return false;
node = node[word[i]];
}
return node.isEnd === true;
};
📘 Trie.prototype.startsWith = function (prefix) {
let node = this.root;
for (let i = 0; i < prefix.length; i++) {
if (!node[prefix[i]]) return false;
node = node[prefix[i]];
}
return true;
};
Add & Search Word #211 📘
❓: Design a data structure that supports adding new words & finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary() Initializes the object.
void addWord(word) Adds word to the data structure, it can be matched later.
bool search(word) Returns true if there is any string in the data structure that matches word or false otherwise. word may contain dots '.' where dots can be matched with any letter.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: ["WordDictionary","addWord","addWord","addWord","search","search","search","search"] Output: [null,null,null,null,false,true,true,true] Explain: WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary(); wordDictionary.addWord("bad"); wordDictionary.addWord("dad"); wordDictionary.addWord("mad"); wordDictionary.search("pad"); // return False wordDictionary.search("bad"); // return True wordDictionary.search(".ad"); // return True wordDictionary.search("b.."); // return True
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📘 Trie ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var WordDictionary = function () {
this.root = {};
};
WordDictionary.prototype.addWord = function (word) {
let node = this.root;
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
if (!node[word[i]]) node[word[i]] = {};
node = node[word[i]];
}
node.isEnd = true;
};
WordDictionary.prototype.search = function (word) {
let node = this.root;
function 🌲 DFS(node, i) {
if (i === word.length) return node.isEnd === true;
if (word[i] === '.') {
for (let key in node) {
if (🌲 DFS(node[key], i + 1)) return true;
}
} else {
if (!node[word[i]]) return false;
return 🌲 DFS(node[word[i]], i + 1);
}
}
return 🌲 DFS(node, 0);
};
Word Search II #212 📘
❓: Given an m x n board of characters & a list of strings words, return all words on the board. Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] Output: ["eat","oath"] 2️⃣ Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"] Output: []
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: 📘 Trie ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var findWords = function (board, words) {
let result = [];
let root = {};
for (let word of words) {
let node = root;
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
if (!node[word[i]]) node[word[i]] = {};
node = node[word[i]];
}
node.isEnd = true;
}
let m = board.length;
let n = board[0].length;
let visited = new Array(m).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n).fill(false));
function 🌲 DFS(node, i, j, str) {
if (node.isEnd) {
result.push(str);
node.isEnd = false;
}
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || visited[i][j]) return;
if (!node[board[i][j]]) return;
visited[i][j] = true;
🌲 DFS(node[board[i][j]], i + 1, j, str + board[i][j]);
🌲 DFS(node[board[i][j]], i - 1, j, str + board[i][j]);
🌲 DFS(node[board[i][j]], i, j + 1, str + board[i][j]);
🌲 DFS(node[board[i][j]], i, j - 1, str + board[i][j]);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (root[board[i][j]]) 🌲 DFS(root[board[i][j]], i, j, board[i][j]);
}
}
return result;
};
Pattern Used: Heap
❓: You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order. Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list & return it.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 2️⃣ Input: lists = [] Output: [] 3️⃣ Input: lists = [[]] Output: []
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: Heap ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
import ListNode from "DataStructures/LinkedList/ListNode.js";
import MinHeap from "DataStructures/Heaps/MinHeap.js";
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
if (lists.length === 0) return null;
let dummy = new ListNode();
let curr = dummy;
let minHeap = new MinHeap();
for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
if (lists[i]) minHeap.insert(lists[i]);
}
while (minHeap.size() > 0) {
let node = minHeap.remove();
curr.next = node;
curr = curr.next;
if (node.next) minHeap.insert(node.next);
}
return dummy.next;
};
Top K Frequent Elements #347 👑
Pattern Used: K TOP 👑
❓: Given an integer array nums & an integer k, return the k most frequent elements. You may return the answer in any order.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 Output: [1,2] 2️⃣ Input: nums = [1], k = 1 Output: [1]
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: Heap ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
import MinHeap from './DataStructures/Heap/MinHeap.js';
function findLargestKNum(nums, k) {
const minHeap = new MinHeap();
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
minHeap.push(nums[i]);
}
for (i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > minHeap.peek()) {
minHeap.pop();
minHeap.push(nums[i]);
}
}
return minHeap.toArray();
}
Pattern Used: Heap
❓: Median is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value & the median is the mean of the two middle values. For example, for arr = [2,3,4], the median is 3. For example, for arr = [2,3], the median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5. Implement the MedianFinder class: MedianFinder() initializes the MedianFinder object. void addNum(num) adds the integer num from the data stream to the data structure. double findMedian() returns the median of all elements so far. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
🐣: 1️⃣ Input: ["MedianFinder", "addNum", "addNum", "findMedian", "addNum", "findMedian"] [[], [1], [2], [], [3], []] Output: [null, null, null, 1.5, null, 2.0] 2️⃣ Input: ["MedianFinder", "addNum", "findMedian", "addNum", "findMedian"] [[], [2], [], [3], []] Output: [null, null, 2.0, null, 2.5
🐢 Solution: 🔨 Brute Force ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
🐇 Solution: Heap ⏰: O(n) 🪐: O(n)
var MedianFinder = function () {
this.minHeap = new MinHeap();
this.maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
};
MedianFinder.prototype.addNum = function (num) {
if (this.minHeap.size() === 0 || num > this.minHeap.peek()) {
this.minHeap.insert(num);
} else {
this.maxHeap.insert(num);
}
if (this.minHeap.size() - this.maxHeap.size() > 1) {
this.maxHeap.insert(this.minHeap.extract());
} else if (this.maxHeap.size() - this.minHeap.size() > 1) {
this.minHeap.insert(this.maxHeap.extract());
}
};
MedianFinder.prototype.findMedian = function () {
if (this.minHeap.size() === this.maxHeap.size()) {
return (this.minHeap.peek() + this.maxHeap.peek()) / 2;
} else if (this.minHeap.size() > this.maxHeap.size()) {
return this.minHeap.peek();
} else {
return this.maxHeap.peek();
}
};
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
peek() {
return this.heap[0];
}
insert(val) {
this.heap.push(val);
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp() {
let idx = this.heap.length - 1;
while (idx > 0) {
let parentIdx = Math.floor((idx - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[parentIdx] > this.heap[idx]) {
[this.heap[parentIdx], this.heap[idx]] = [
this.heap[idx],
this.heap[parentIdx],
];
idx = parentIdx;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
extract() {
let min = this.heap[0];
let end = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = end;
this.sinkDown();
}
return min;
}
sinkDown() {
let idx = 0;
let length = this.heap.length;
let element = this.heap[0];
while (true) {
let leftChildIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
let rightChildIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
let leftChild, rightChild;
let swap = null;
if (leftChildIdx < length) {
leftChild = this.heap[leftChildIdx];
if (leftChild < element) {
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
if (rightChildIdx < length) {
rightChild = this.heap[rightChildIdx];
if (
(swap === null && rightChild < element) ||
(swap !== null && rightChild < leftChild) ) {
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
if (swap === null) break;
this.heap[idx] = this.heap[swap];
this.heap[swap] = element;
idx = swap;
}
}
}
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
peek() {
return this.heap[0];
}
insert(val) {
this.heap.push(val);
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp() {
let idx = this.heap.length - 1;
while (idx > 0) {
let parentIdx = Math.floor((idx - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[parentIdx] < this.heap[idx]) {
[this.heap[parentIdx], this.heap[idx]] = [
this.heap[idx],
this.heap[parentIdx],
];
idx = parentIdx;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
extract() {
let max = this.heap[0];
let end = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = end;
this.sinkDown();
}
return max;
}
sinkDown() {
let idx = 0;
let length = this.heap.length;
let element = this.heap[0];
while (true) {
let leftChildIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
let rightChildIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
let leftChild, rightChild;
let swap = null;
if (leftChildIdx < length) {
leftChild = this.heap[leftChildIdx];
if (leftChild > element) {
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
if (rightChildIdx < length) {
rightChild = this.heap[rightChildIdx];
if (
(swap === null && rightChild > element) ||
(swap !== null && rightChild > leftChild) ) {
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
if (swap === null) break;
this.heap[idx] = this.heap[swap];
this.heap[swap] = element;
idx = swap;
}
}
}
912. Sort an Array
922. Sort Array By Parity II
973. K Closest Points to Origin
977. Squares of a Sorted Array
1470. Shuffle the Array
1480. Running Sum of 1d Array
1512. Number of Good Pairs
1672. Richest Customer Wealth
1678. Goal Parser Interpretation
1720. Decode XORed Array
1721. Swapping Nodes in a Linked List
1742. Maximum Number of Balls in a Box
1773. Count Items Matching a Rule
1812. Determine Color of a Chessboard Square
1822. Sign of the Product of an Array
1828. Queries on Number of Points Inside a Circle
1832. Check if the Sentence Is Pangram
1846. Maximum Element After Decreasing & Rearranging
1854. Maximum Population Year
1869. Longer Contiguous Segments of Ones than Zeros
1877. Minimize Maximum Pair Sum in Array
1880. Check if Word Equals Summation of Two Words
1886. Determine Whether Matrix Can Be Obtained By Rotation
1893. Check if All the Integers in a Range Are Covered
1894. Find the Student that Will Replace the Chalk
1898. Maximum Number of Removable Characters
1903. Largest Odd Number in String
1909. Remove One Element to Make the Array Strictly Increasing
1913. Maximum Product Difference Between Two Pairs
1917. Maximum Alternating Subsequence Sum
1920. Build Array from Permutation
1921. Eliminate Maximum Number of Monsters
1. What is the input?
2. What is the output?
3. What is the constraint?
4. What is the edge case?
5. What is the 🔨 Brute Force solution?
6. What is the optimal solution?
7. What is the ⏰ of the 🔨 Brute Force solution?
8. What is the ⏰ of the optimal solution?
9. What is the 🪐 of the 🔨 Brute Force solution?
10. What is the 🪐 of the optimal solution?
11. What is the data structure to use?
12. What is the algorithm to use?
Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Minimum Window Substring
Longest Substring with At Most Two Distinct Characters
Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters
Longest Repeating Character Replacement
Longest Substring with At Least K Repeating Characters
Permutation in String
Find All Anagrams in a String
Substring with Concatenation of All Words
Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Longest Subarray of 1's After Deleting One Element
Maximum Number of Vowels in a Substring of Given Length
Replace the Substring for Balanced String
Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters \
Two Sum
3Sum
3Sum Smaller
4Sum
4Sum II
Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
Two Sum III - Data structure design
Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
Two Sum Less Than K
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
Remove Element
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
Remove Linked List Elements
Remove Nth Node From End of List
Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List II
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Swap Nodes in Pairs
Partition List
Sort List \
Linked List Cycle
Linked List Cycle II
Palindrome Linked List
Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Middle of the Linked List
Remove Nth Node From End of List
Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List II
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Swap Nodes in Pairs
Sort List
Linked List Cycle
Linked List Cycle II
Palindrome Linked List
Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Middle of the Linked List
Remove Nth Node From End of List
Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List II
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Swap Nodes in Pairs
Sort List \
Merge Intervals
Insert Interval
Non-overlapping Intervals
Meeting Rooms
Meeting Rooms II
Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons
Range Module
Add Bold Tag in String
Insert Delete GetR&om O(1)
Insert Delete GetR&om O(1) - Duplicates allowed
Data Stream as DisjoIntervals
Summary Ranges
Summary Ranges II
Employee Free Time
Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons
Range Module
Add Bold Tag in String
Insert Delete GetR&om O(1)
Insert Delete GetR&om O(1) - Duplicates allowed
Data Stream as DisjoIntervals
Summary Ranges\
Find the Duplicate Number
Find All Duplicates in an Array
Find the Missing Number
Find the Smallest Missing Positive Number
Find the Corrupt Pair
Find All Missing Numbers
Find the First K Missing Positive Numbers
Find the First Missing Positive Number
Find the Duplicate Number
Find All Duplicates in an Array
Find the Missing Number
Find the Smallest Missing Positive Number
Find the Corrupt Pair
Find All Missing Numbers
Find the First K Missing Positive Numbers
Find the First Missing Positive Number \
Reverse a Sub-list
Reverse every K-element Sub-list
Reverse Alternating K-element Sub-list
Reverse a Sub-list
Reverse every K-element Sub-list
Reverse Alternating K-element Sub-list \
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II \
Binary Tree Path Sum
All Paths for a Sum
Sum of Path Numbers
Path With Given Sequence
Count Paths for a Sum
Binary Tree Path Sum
All Paths for a Sum
Sum of Path Numbers
Path With Given Sequence
Count Paths for a Sum \
Find the Median of a Number Stream
Sliding Window Median
Find the Median of a Number Stream
Sliding Window Median \
Subsets
Subsets With Duplicates
Permutations
Permutations With Duplicates
String Permutations by changing case
Balanced Parentheses
Unique Generalized Abbreviations
Subsets
Subsets With Duplicates
Permutations
Permutations With Duplicates
String Permutations by changing case
Balanced Parentheses
Unique Generalized Abbreviations \
Order-agnostic 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search
Ceiling of a Number
Next Letter
Number Range
Search in a Sorted Infinite Array
Minimum Difference Element
Bitonic Array Maximum
Order-agnostic 🏁🔚 Mod Binary Search
Ceiling of a Number
Next Letter
Number Range
Search in a Sorted Infinite Array
Minimum Difference Element
Bitonic Array Maximum \
Kth Smallest Number
Kth Largest Number
Connect Ropes
Top 'K' Frequent Numbers
K Closest Points to the Origin
Kth Smallest Number
Kth Largest Number
Connect Ropes
Top 'K' Frequent Numbers
K Closest Points to the Origin \
Merge K Sorted Lists
Kth Smallest Number in M Sorted Lists
Kth Smallest Number in a Sorted Matrix
Smallest Number Range
Merge K Sorted Lists
Kth Smallest Number in M Sorted Lists
Kth Smallest Number in a Sorted Matrix
Smallest Number Range \
Tasks Scheduling
Tasks Scheduling Order
All Tasks Scheduling Orders
Tasks Scheduling
Tasks Scheduling Order
All Tasks Scheduling Orders \
Equal Subset Sum Partition
Subset Sum
Minimum Subset Sum Difference
Count of Subset Sum
Minimum Subset Sum Difference
Count of Subset Sum \
Single Number
Find the Corrupt Pair
Complement of Base 10 Number
Bitwise & of Numbers Range
Single Number
Find the Corrupt Pair
Complement of Base 10 Number
Bitwise & of Numbers Range \
. . . .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
. . .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
. .
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
. .
.
. . .
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. . .
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.