Important
The domain for ingredients is being switched from "ingredients.tech" to "ingredients.work". Requests to the old domain will be redirected.
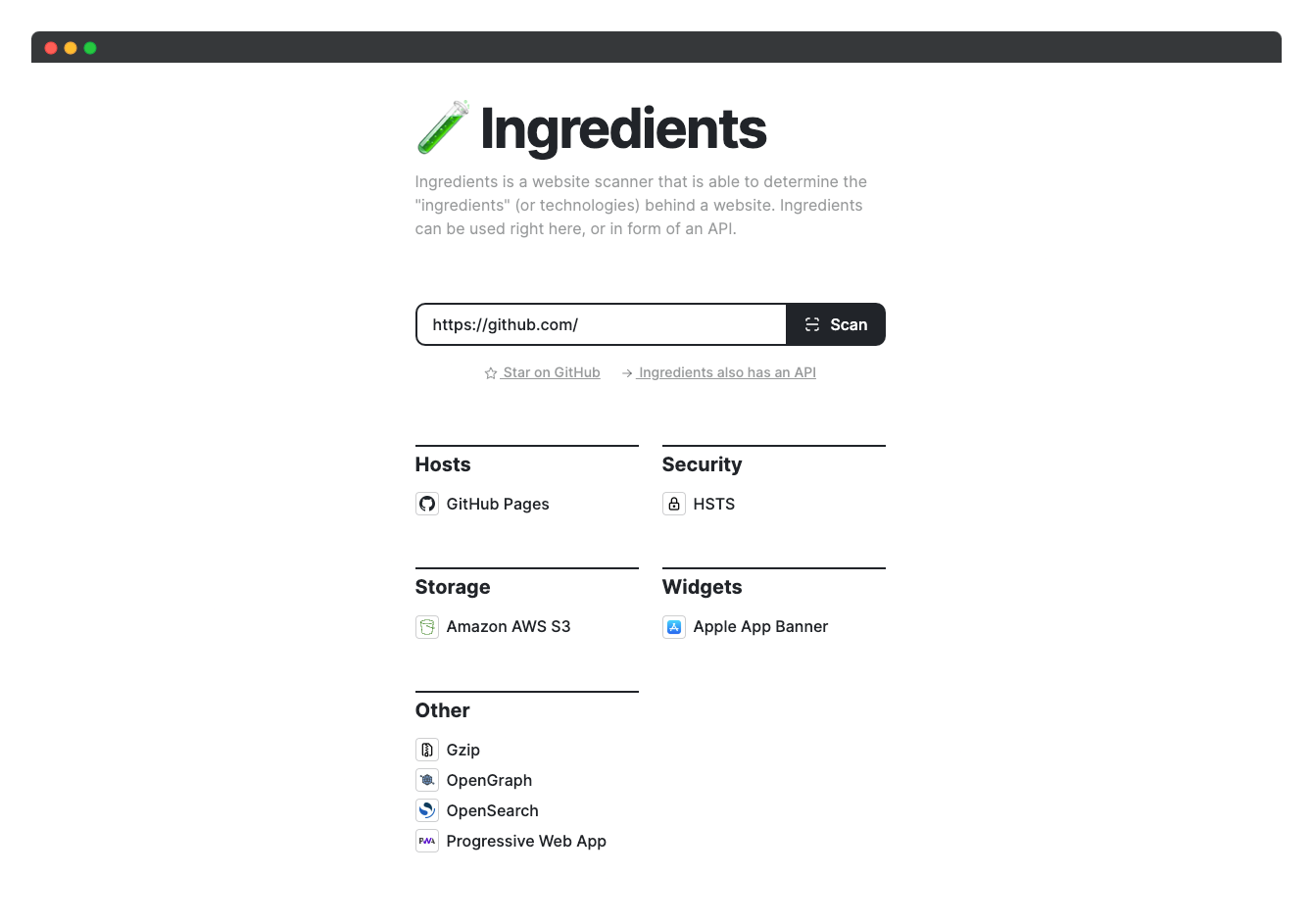
Ingredients is a website scanner that is able to determine the "ingredients" (or technologies) behind a website.
It helps users discover the various software, frameworks, content management systems, analytics tools, and other technologies that are used to build and maintain a particular website.
Ingredients consists of a frontend application (made with SvelteKit) and an API (made with FastAPI) with a simple script, that requests websites and checks their HTML tags and HTTP headers based on filters. The filters or "ingredients" are stored in their respective category-folders in the ingredients/ folder.
Each "ingredient" consists of a JSON file like the following:
{
"name": "Ingredient Name",
"description": "Short description of the ingredient",
"icon": "/icon/ingredient-name.png",
"checks": {
"tags": [
{
"tag": "script",
"attribute": "src",
"value": "cdn.example.com"
},
{
"tag": "script",
"attribute": null,
"value": "cdn.example.com"
}
],
"headers": [
{
"header": "Server",
"value": "example"
},
{
"header": "Request-Id",
"value": null
}
]
}
}In the JSON file, you can define the HTML tags and HTTP headers the script should look for, to identify, if a website is using the ingredient.
As you can also see, this JSON file mentions a path to an icon, which is used to visualize the ingredient. Each favicon has a resolution of 32x32 pixels and is located inside the icons/ folder.
Ingredients has an API you can use. This API can be used to scan sites.
Note
The API has a set of CORS origins in place as of now, so might only work locally! This might change later.
You can start a scan with one GET call. Just provide the URL you want to scan as a query parameter.
GET https://api.ingredients.work/ingredients?url=https://example.comNote
Before you contribute, please take a look at the CONTRIBUTING.md file
To add an ingredient, create a JSON file in ingredients/ folder inside a fitting category-folder and add its icon (size 32x32 pixels, .png format) in the icons/ folder.
When defining an ingredient, follow this template:
{
"name": "Ingredient Name",
"description": "Short description of the ingredient",
"icon": "/icon/ingredient-name.png",
"checks": {
"tags": [
(TAG CHECKS GO HERE)
],
"headers": [
(HEADER CHECKS GO HERE)
]
}
}Tag checks are filters, which search for specific HTML tags on a website, to identify if it's using the ingredient. Here's an example:
{
"tag": "script",
"attribute": "src",
"value": "cdn.example.com"
}Here, we're checking if the website has any <script> tags, which have cdn.example.com inside their src attribute.
And here, we're not defining an attribute (using null). This means, we're checking if the inside of the <script> tag has cdn.example.com inside:
{
"tag": "script",
"attribute": null,
"value": "cdn.example.com"
}Like the following:
<script>
const url = "cdn.example.com"
</script>Tag checks can also use wildcard values. For instance, if you need to check if a <script> tag's src attribute contains a domain and a file extension, you can do so with an asterisk (*). This will split your check into multiple segments. All segments must be inside the checked tag attribute somewhere. For example:
{
"tag": "script",
"attribute": "src",
"value": "example.com/library/*.js"
}This will check if the src attribute of a <script> tag includes example.com/library/ and .js.
Header checks are filters, which search for specific HTTP response headers when requesting the website, to identify if it's using the ingredient. Here's an example:
{
"header": "Server",
"value": "example"
}Here, we're checking if the HTTP response headers include a header called Server which has the value example inside.
And here, we're not defining a header value (using null). This means, we're checking if the Request-Id header exists at all, without explicitly checking for its value:
{
"header": "Request-Id",
"value": null
}Ingredients — Website Technology Scanner
Copyright (C) 2023 Paul Haedrich (berrysauce)
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Affero General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License along with this program. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.