Convolutional neural network-based prediction of drug mechanism-of-action (MoA) from high content screening images and use of CNN image embeddings to find outliers/novel images.
Fluorescence microscopy is a core tool in biological and drug discovery. High content screening automates fluorescence microscopy on a mass scale, allowing researchers to understand the impact of thousands of perturbations on cellular morphology and health in a single assay. Screens specifically focused on treatment of cells with biologically active molecules / drugs can lend insight into the function of those compounds based on how they modulate the imaged cellular structures. Functional insights can lead to identification of compound "hits" for potential drug candidates.
See the BBBC021 landing page for more info on the dataset.
tl;dr:
- Human breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) treated with various compounds of both known and unknown MoA.
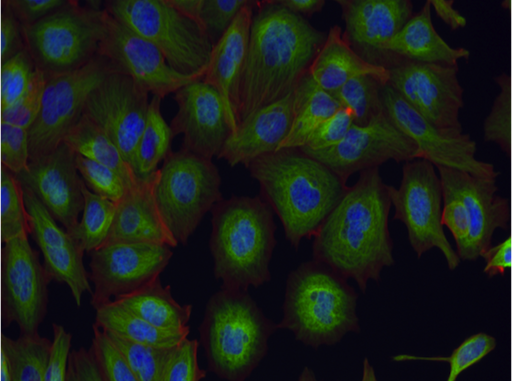
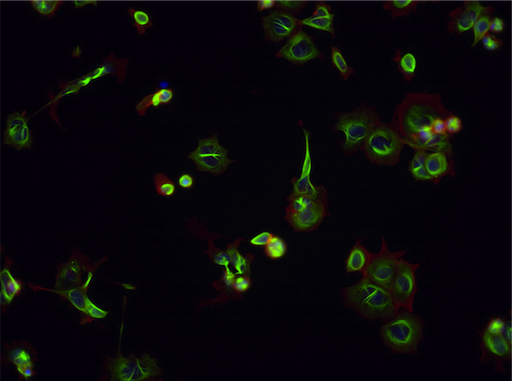
- Following treatment, cells are stained for their nuclei (blue) and the cytoskeletal proteins tubulin (green) and actin (red).
| Aurora kinase inhibitor | Tubulin stabilizer | Eg5 inhibitor |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
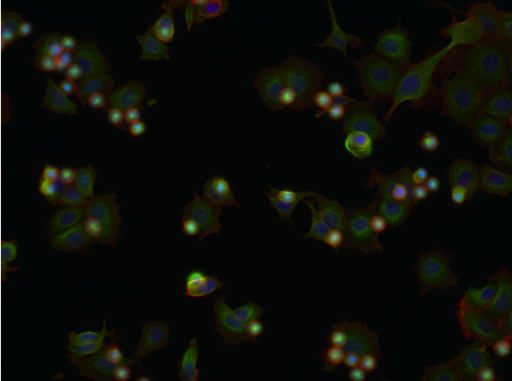 |
Example images from BBBC021.
- Given a multi-channel fluorescence image of MCF-7 cells, train a convolutional neural network to predict the mechanism-of-action of the compound the cells were treated with.
- Use the trained CNN to extract image embeddings.
- Perform UMAP dimensionality reduction on embeddings for dataset visualization and exploration.
- Find interesting / artifactual image outliers in the BBBC021 dataset using image embeddings.
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/zbarry/pytorch-hcs.git
- Install the environment and the
pytorch_hcspackage:
cd pytorch-hcs
conda install -c conda-forge mamba -y
mamba env update
(the mamba install is optional but recommended as a conda replacement which has much faster dependency solves)
This will create a pytorch-hcs environment and pip install the Python package in one go.
A fork of pybbbc will also be installed. We use this to download the BBBC021 dataset and access individual images and metadata.
- Acquire the BBBC021 dataset
Either run notebooks/download_bbbc021.ipynb from top to bottom or in a Python terminal (with the pytorch-hcs environment activated):
from pybbbc import BBBC021
BBBC021.download()
BBBC021.make_dataset(max_workers=2)
# test
bbbc021 = BBBC021()
bbbc021[0]There are a lot of files to download. Plan on this process taking hours.
- PyTorch and PyTorch-Lightning - PTL reduces training boilerplate.
- Weights and Biases - stores training runs and model checkpoints.
Reusable code modules are found in the pytorch_hcs package.
datasets.py- PyTorch dataset and PyTorch-Lightning DataModule for working with BBBC021 data.models.py- PyTorch-Lightning modules wrapping CNN models.transforms.py- image transforms for data augmentation.
The code that orchestrates the modules found in the Python package is in notebooks in the notebooks/ folder.
01_download_bbbc021.ipynb- download raw BBBC021 images and pre-process them using pybbbc.02_bbbc021_visualization.ipynb- explore the BBBC021 dataset with an interactive visualization.03_train_model.ipynb- train a CNN to predict MoA from BBBC021 images.04_evaluate_model.ipynb- evaluate performance of trained CNN on test set.05_visualize_embeddings.ipynb- produce image embeddings, UMAP them, visualize and find outliers.
dataset_cleaning_visualization.ipynb- manually step through BBBC021 with a visualization to label images in the training and validation sets as "good" or "bad".notebooks/analysis/umap_param_sweep.ipynb- sweep through UMAP parameterizations to assess impact on resulting embeddings.
These will clear notebook outputs as well as run code formatters upon commit.
pre-commit install
- Decrease plate effects on embeddings (e.g., through adversarial learning).
- Add hyperparameter sweep capability using Weights and Biases / improve model classification performance.
- Log model test set evaluation results to W&B.
- Make better use of W&B in general for tracking results.
- Move BBBC021 dataset to ActiveLoop Hub to speed up download / dataset prep times.
- Try out a k-fold cross validation strategy.